The battle of marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugateGreece. The Greek army decisively defeated the more numerous Persians, marking a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars.
The first Persian invasion was a response to Greek involvement in the Ionian Revolt, when Athens and Eretria had sent a force to support the cities of Ionia in their attempt to overthrow Persian rule. The Athenians and Eretrians had succeeded in capturing and burning Sardis, but they were then forced to retreat with heavy losses. In response to this raid, Darius swore to burn down Athens and Eretria. According to Herodotus, Darius asked for his bow, he placed an arrow upon the string and he discharged it upwards towards heaven, and as he shot into the air he said: "Zeus, grant me to take vengeance upon the Athenians!". Also he charged one of his servants, to say to him, every day before dinner, three times: "Master, remember the Athenians."
At the time of the battle, Sparta and Athens were the two largest city states. Once the Ionian revolt was finally crushed by the Persian victory at the Battle of Lade in 494 BC, Darius began plans to subjugate Greece. In 490 BC, he sent a naval task force under Datis and Artaphernes across the Aegean, to subjugate the Cyclades, and then to make punitive attacks on Athens and Eretrea. Reaching Euboea in mid-summer after a successful campaign in the Aegean, the Persians proceeded to besiege and capture Eretria. The Persian force then sailed for Attica, landing in the bay near the town of Marathon. The Athenians, joined by a small force from Plataea, marched to Marathon, and succeeded in blocking the two exits from the plain of Marathon.
The Greeks could not hope to face the superior Persian cavalry; however, when learning that the Persian cavalry was temporarily absent from the camp, Miltiades ordered a general attack against the Persians. He reinforced his flanks, luring the Persians' best fighters into his centre. The inward wheeling flanks enveloped the Persians, routing them. The Persian army broke in panic towards their ships, and large numbers were slaughtered. The defeat at Marathon marked the end of the first Persian invasion of Greece, and the Persian force retreated to Asia. Darius then began raising a huge new army with which he meant to completely subjugate Greece; however, in 486 BC, his Egyptian subjects revolted, indefinitely postponing any Greek expedition. After Darius died, his son Xerxes I restarted the preparations for a second invasion of Greece, which finally began in 480 BC.
The Battle of Marathon was a watershed in the Greco-Persian wars, showing the Greeks that the Persians could be beaten; the eventual Greek triumph in these wars can be seen to begin at Marathon. Since the following two hundred years saw the rise of the Classical Greek civilization, which has been enduringly influential in western society, the Battle of Marathon is often seen as a pivotal moment in European history. The battle is perhaps now more famous as the inspiration for the marathon race. Although thought to be historically inaccurate, the legend of the Greek messenger Pheidippides running to Athens with news of the victory became the inspiration for this athletic event, introduced at the 1896 Athens Olympics, and originally run between Marathon and Athens.
Herodotus does not give a figure for the size of the Athenian army. However, Cornelius Nepos, Pausanias and Plutarchall give the figure of 9,000 Athenians and 1,000 Plataeans; while Justin suggests that there were 10,000 Athenians and 1,000 Plataeans. These numbers are highly comparable to the number of troops Herodotus says that the Athenians and Plataeans sent to the Battle of Plataea 11 years later. Pausanias noticed on the monument to the battle the names of former slaves who were freed in exchange for military services. Modern historians generally accept these numbers as reasonable.
Persians[edit]For a full discussion of the size of the Persian invasion force, see First Persian invasion of Greece According to Herodotus, the fleet sent by Darius consisted of 600 triremes. Herodotus does not estimate the size of the Persian army, only saying that they were a "large infantry that was well packed". Among ancient sources, the poet Simonides, another near-contemporary, says the campaign force numbered 200,000; while a later writer, the Roman Cornelius Nepos estimates 200,000 infantry and 10,000 cavalry, of which only 100,000 fought in the battle, while the rest were loaded into the fleet that was rounding Cape Sounion; Plutarch and Pausanias both independently give 300,000, as does the Suda dictionary. Plato and Lysias give 500,000; and Justinus 600,000.
Modern historians have proposed wide ranging numbers for the infantry, from 20,000–100,000 with a consensus of perhaps 25,000; estimates for the cavalry are in the range of 1,000.
From a strategic point of view, the Athenians had some disadvantages at Marathon. In order to face the Persians in battle, the Athenians had to summon all available hoplites; and even then they were still probably outnumbered at least 2 to 1. Furthermore, raising such a large army had denuded Athens of defenders, and thus any secondary attack in the Athenian rear would cut the army off from the city; and any direct attack on the city could not be defended against. Still further, defeat at Marathon would mean the complete defeat of Athens, since no other Athenian army existed. The Athenian strategy was therefore to keep the Persian army pinned down at Marathon, blocking both exits from the plain, and thus preventing themselves from being outmaneuvered. However, these disadvantages were balanced by some advantages. The Athenians initially had no need to seek battle, since they had managed to confine the Persians to the plain of Marathon. Furthermore, time worked in their favour, as every day brought the arrival of the Spartans closer. Having everything to lose by attacking, and much to gain by not attacking, the Athenians remained on the defensive in the run up to the battle. Tactically, hoplites were vulnerable to attacks by cavalry, and since the Persians had substantial numbers of cavalry, this made any offensive maneuver by the Athenians even more of a risk, and thus reinforced the defensive strategy of the Athenians.
The Persian strategy, on the other hand, was probably principally determined by tactical considerations. The Persian infantry was evidently lightly armoured, and no match for hoplites in a head-on confrontation (as would be demonstrated at the later battles of Thermopylae and Plataea.) Since the Athenians seem to have taken up a strong defensive position at Marathon, the Persian hesitance was probably a reluctance to attack the Athenians head-on.
Whatever event eventually triggered the battle, it obviously altered the strategic or tactical balance sufficiently to induce the Athenians to attack the Persians. If the first theory is correct (see above), then the absence of cavalry removed the main Athenian tactical disadvantage, and the threat of being outflanked made it imperative to attack. Conversely, if the second theory is correct, then the Athenians were merely reacting to the Persians attacking them. Since the Persian force obviously contained a high proportion of missile troops, a static defensive position would have made little sense for the Athenians;\ the strength of the hoplite was in the melee, and the sooner that could be brought about, the better, from the Athenian point of view. If the second theory is correct, this raises the further question of why the Persians, having hesitated for several days, then attacked. There may have been several strategic reasons for this; perhaps they were aware (or suspected) that the Athenians were expecting reinforcements. Alternatively, since they may have felt the need to force some kind of victory—they could hardly remain at Marathon indefinitely.
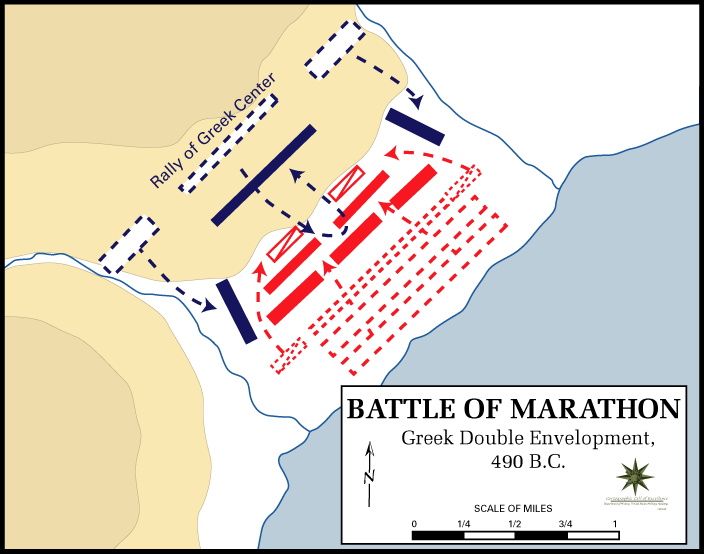
The distance between the two armies at the point of battle had narrowed to "a distance not less than 8 stadia" or about 1,500 meters. Miltiades ordered the two tribes that were forming the center of the Greek formation, the Leontis tribe led by Themistocles and the Antiochis tribe led by Aristides, to be arranged in the depth of four ranks while the rest of the tribes at their flanks were in ranks of eight. Some modern commentators have suggested this was a deliberate ploy to encourage a double envelopment of the Persian centre. However, this supposes a level of training that the Greeks did not possess. There is little evidence for any such tactical thinking in Greek battles until Leuctra in 371 BC. It is therefore probable that this arrangement was made, possibly at the last moment, so that the Athenian line was as long as the Persian line, and would not therefore be outflanked.
Map showing the armies' main movements during the battle
When the Athenian line was ready, according to one source, the simple signal to advance was given by Miltiades: "At them".Herodotus implies the Athenians ran the whole distance to the Persian lines, shouting their ululating war cry, "Ελελευ! Ελελευ!" ("Eleleu! Eleleu!"). It is doubtful that the Athenians ran the whole distance; in full armour this would be very difficult. More likely, they marched until they reached the limit of the archers' effectiveness, the "beaten zone" (roughly 200 meters), and then broke into a run towards their enemy. Another possibility is that they ran up to the 200 meter-mark in broken ranks, and then reformed for the march into battle from there. Herodotus suggests that this was the first time a Greek army ran into battle in this way; this was probably because it was the first time that a Greek army had faced an enemy composed primarily of missile troops. All this was evidently much to the surprise of the Persians; "... in their minds they charged the Athenians with madness which must be fatal, seeing that they were few and yet were pressing forwards at a run, having neither cavalry nor archers". Indeed, based on their previous experience of the Greeks, the Persians might be excused for this; Herodotus tells us that the Athenians at Marathon were "first to endure looking at Median dress and men wearing it, for up until then just hearing the name of the Medes caused the Hellenes to panic". Passing through the hail of arrows launched by the Persian army, protected for the most part by their armour, the Greek line finally collided with the enemy army. Holland provides an evocative description:
The enemy directly in their path ... realised to their horror that [the Athenians], far from providing the easy pickings for their bowmen, as they had first imagined, were not going to be halted ... The impact was devastating. The Athenians had honed their style of fighting in combat with other phalanxes, wooden shields smashing against wooden shields, iron spear tips clattering against breastplates of bronze ... in those first terrible seconds of collision, there was nothing but a pulverizing crash of metal into flesh and bone; then the rolling of the Athenian tide over men wearing, at most, quilted jerkins for protection, and armed, perhaps, with nothing more than bows or slings. The hoplites' ash spears, rather than shivering ... could instead stab and stab again, and those of the enemy who avoided their fearful jabbing might easily be crushed to death beneath the sheer weight of the advancing men of bronze.
The Athenian wings quickly routed the inferior Persian levies on the flanks, before turning inwards to surround the Persian centre, which had been more successful against the thin Greek centre. The battle ended when the Persian centre then broke in panic towards their ships, pursued by the Greeks. Some, unaware of the local terrain, ran towards the swamps where unknown numbers drowned. The Athenians pursued the Persians back to their ships, and managed to capture seven ships, though the majority were able to launch successfully. Herodotus recounts the story that Cynaegirus, brother of the playwright Aeschylus, who was also among the fighters, charged into the sea, grabbed one Persian trireme, and started pulling it towards shore. A member of the crew saw him, cut off his hand, and Cynaegirus died.
Herodotus records that 6,400 Persian bodies were counted on the battlefield, and it is unknown how many more perished in the swamps. The Athenians lost 192 men and the Plataeans 11. Among the dead were the war archon Callimachus and the general Stesilaos.
In the immediate aftermath of the battle, Herodotus says that the Persian fleet sailed around Cape Sounion to attack Athens directly. As has been discussed above, some modern historians place this attempt just before the battle. Either way, the Athenians evidently realised that their city was still under threat, and marched as quickly as possible back to Athens. The two tribes which had been in the centre of the Athenian line stayed to guard the battlefield under the command of Aristides. The Athenians arrived in time to prevent the Persians from securing a landing, and seeing that the opportunity was lost, the Persians turned about and returned to Asia. Connected with this episode, Herodotus recounts a rumour that this manoeuver by the Persians had been planned in conjunction with the Alcmaeonids, the prominent Athenian aristocratic family, and that a "shield-signal" had been given after the battle. Although many interpretations of this have been offered, it is impossible to tell whether this was true, and if so, what exactly the signal meant. On the next day, the Spartan army arrived at Marathon, having covered the 220 kilometers (140 mi) in only three days. The Spartans toured the battlefield at Marathon, and agreed that the Athenians had won a great victory.
Mound (soros) in which the Athenian dead were buried after the Battle of Marathon
The dead of Marathon were buried on the battlefield. On the tomb of the Athenians this epigram composed by Simonides was written:
Fighting in the forefront of the Hellenes, the Athenians at Marathon destroyed the might of the gold-bearing Medes.In the meanwhile, Darius began raising a huge new army with which he meant to completely subjugate Greece; however, in 486 BC, his Egyptian subjects revolted, indefinitely postponing any Greek expedition. Darius then died whilst preparing to march on Egypt, and the throne of Persia passed to his son Xerxes I. Xerxes crushed the Egyptian revolt, and very quickly restarted the preparations for the invasion of Greece. The epic second Persian invasion of Greece finally began in 480 BC, and the Persians met with initial success at the battles of Thermopylae and Artemisium. However, defeat at the Battle of Salamis would be the turning point in the campaign, and the next year the expedition was ended by the decisive Greek victory at the Battle of Plataea.
The first Persian invasion was a response to Greek involvement in the Ionian Revolt, when Athens and Eretria had sent a force to support the cities of Ionia in their attempt to overthrow Persian rule. The Athenians and Eretrians had succeeded in capturing and burning Sardis, but they were then forced to retreat with heavy losses. In response to this raid, Darius swore to burn down Athens and Eretria. According to Herodotus, Darius asked for his bow, he placed an arrow upon the string and he discharged it upwards towards heaven, and as he shot into the air he said: "Zeus, grant me to take vengeance upon the Athenians!". Also he charged one of his servants, to say to him, every day before dinner, three times: "Master, remember the Athenians."
At the time of the battle, Sparta and Athens were the two largest city states. Once the Ionian revolt was finally crushed by the Persian victory at the Battle of Lade in 494 BC, Darius began plans to subjugate Greece. In 490 BC, he sent a naval task force under Datis and Artaphernes across the Aegean, to subjugate the Cyclades, and then to make punitive attacks on Athens and Eretrea. Reaching Euboea in mid-summer after a successful campaign in the Aegean, the Persians proceeded to besiege and capture Eretria. The Persian force then sailed for Attica, landing in the bay near the town of Marathon. The Athenians, joined by a small force from Plataea, marched to Marathon, and succeeded in blocking the two exits from the plain of Marathon.
The Greeks could not hope to face the superior Persian cavalry; however, when learning that the Persian cavalry was temporarily absent from the camp, Miltiades ordered a general attack against the Persians. He reinforced his flanks, luring the Persians' best fighters into his centre. The inward wheeling flanks enveloped the Persians, routing them. The Persian army broke in panic towards their ships, and large numbers were slaughtered. The defeat at Marathon marked the end of the first Persian invasion of Greece, and the Persian force retreated to Asia. Darius then began raising a huge new army with which he meant to completely subjugate Greece; however, in 486 BC, his Egyptian subjects revolted, indefinitely postponing any Greek expedition. After Darius died, his son Xerxes I restarted the preparations for a second invasion of Greece, which finally began in 480 BC.
The Battle of Marathon was a watershed in the Greco-Persian wars, showing the Greeks that the Persians could be beaten; the eventual Greek triumph in these wars can be seen to begin at Marathon. Since the following two hundred years saw the rise of the Classical Greek civilization, which has been enduringly influential in western society, the Battle of Marathon is often seen as a pivotal moment in European history. The battle is perhaps now more famous as the inspiration for the marathon race. Although thought to be historically inaccurate, the legend of the Greek messenger Pheidippides running to Athens with news of the victory became the inspiration for this athletic event, introduced at the 1896 Athens Olympics, and originally run between Marathon and Athens.
Herodotus does not give a figure for the size of the Athenian army. However, Cornelius Nepos, Pausanias and Plutarchall give the figure of 9,000 Athenians and 1,000 Plataeans; while Justin suggests that there were 10,000 Athenians and 1,000 Plataeans. These numbers are highly comparable to the number of troops Herodotus says that the Athenians and Plataeans sent to the Battle of Plataea 11 years later. Pausanias noticed on the monument to the battle the names of former slaves who were freed in exchange for military services. Modern historians generally accept these numbers as reasonable.
Persians[edit]For a full discussion of the size of the Persian invasion force, see First Persian invasion of Greece According to Herodotus, the fleet sent by Darius consisted of 600 triremes. Herodotus does not estimate the size of the Persian army, only saying that they were a "large infantry that was well packed". Among ancient sources, the poet Simonides, another near-contemporary, says the campaign force numbered 200,000; while a later writer, the Roman Cornelius Nepos estimates 200,000 infantry and 10,000 cavalry, of which only 100,000 fought in the battle, while the rest were loaded into the fleet that was rounding Cape Sounion; Plutarch and Pausanias both independently give 300,000, as does the Suda dictionary. Plato and Lysias give 500,000; and Justinus 600,000.
Modern historians have proposed wide ranging numbers for the infantry, from 20,000–100,000 with a consensus of perhaps 25,000; estimates for the cavalry are in the range of 1,000.
From a strategic point of view, the Athenians had some disadvantages at Marathon. In order to face the Persians in battle, the Athenians had to summon all available hoplites; and even then they were still probably outnumbered at least 2 to 1. Furthermore, raising such a large army had denuded Athens of defenders, and thus any secondary attack in the Athenian rear would cut the army off from the city; and any direct attack on the city could not be defended against. Still further, defeat at Marathon would mean the complete defeat of Athens, since no other Athenian army existed. The Athenian strategy was therefore to keep the Persian army pinned down at Marathon, blocking both exits from the plain, and thus preventing themselves from being outmaneuvered. However, these disadvantages were balanced by some advantages. The Athenians initially had no need to seek battle, since they had managed to confine the Persians to the plain of Marathon. Furthermore, time worked in their favour, as every day brought the arrival of the Spartans closer. Having everything to lose by attacking, and much to gain by not attacking, the Athenians remained on the defensive in the run up to the battle. Tactically, hoplites were vulnerable to attacks by cavalry, and since the Persians had substantial numbers of cavalry, this made any offensive maneuver by the Athenians even more of a risk, and thus reinforced the defensive strategy of the Athenians.
The Persian strategy, on the other hand, was probably principally determined by tactical considerations. The Persian infantry was evidently lightly armoured, and no match for hoplites in a head-on confrontation (as would be demonstrated at the later battles of Thermopylae and Plataea.) Since the Athenians seem to have taken up a strong defensive position at Marathon, the Persian hesitance was probably a reluctance to attack the Athenians head-on.
Whatever event eventually triggered the battle, it obviously altered the strategic or tactical balance sufficiently to induce the Athenians to attack the Persians. If the first theory is correct (see above), then the absence of cavalry removed the main Athenian tactical disadvantage, and the threat of being outflanked made it imperative to attack. Conversely, if the second theory is correct, then the Athenians were merely reacting to the Persians attacking them. Since the Persian force obviously contained a high proportion of missile troops, a static defensive position would have made little sense for the Athenians;\ the strength of the hoplite was in the melee, and the sooner that could be brought about, the better, from the Athenian point of view. If the second theory is correct, this raises the further question of why the Persians, having hesitated for several days, then attacked. There may have been several strategic reasons for this; perhaps they were aware (or suspected) that the Athenians were expecting reinforcements. Alternatively, since they may have felt the need to force some kind of victory—they could hardly remain at Marathon indefinitely.
The distance between the two armies at the point of battle had narrowed to "a distance not less than 8 stadia" or about 1,500 meters. Miltiades ordered the two tribes that were forming the center of the Greek formation, the Leontis tribe led by Themistocles and the Antiochis tribe led by Aristides, to be arranged in the depth of four ranks while the rest of the tribes at their flanks were in ranks of eight. Some modern commentators have suggested this was a deliberate ploy to encourage a double envelopment of the Persian centre. However, this supposes a level of training that the Greeks did not possess. There is little evidence for any such tactical thinking in Greek battles until Leuctra in 371 BC. It is therefore probable that this arrangement was made, possibly at the last moment, so that the Athenian line was as long as the Persian line, and would not therefore be outflanked.
Map showing the armies' main movements during the battle
When the Athenian line was ready, according to one source, the simple signal to advance was given by Miltiades: "At them".Herodotus implies the Athenians ran the whole distance to the Persian lines, shouting their ululating war cry, "Ελελευ! Ελελευ!" ("Eleleu! Eleleu!"). It is doubtful that the Athenians ran the whole distance; in full armour this would be very difficult. More likely, they marched until they reached the limit of the archers' effectiveness, the "beaten zone" (roughly 200 meters), and then broke into a run towards their enemy. Another possibility is that they ran up to the 200 meter-mark in broken ranks, and then reformed for the march into battle from there. Herodotus suggests that this was the first time a Greek army ran into battle in this way; this was probably because it was the first time that a Greek army had faced an enemy composed primarily of missile troops. All this was evidently much to the surprise of the Persians; "... in their minds they charged the Athenians with madness which must be fatal, seeing that they were few and yet were pressing forwards at a run, having neither cavalry nor archers". Indeed, based on their previous experience of the Greeks, the Persians might be excused for this; Herodotus tells us that the Athenians at Marathon were "first to endure looking at Median dress and men wearing it, for up until then just hearing the name of the Medes caused the Hellenes to panic". Passing through the hail of arrows launched by the Persian army, protected for the most part by their armour, the Greek line finally collided with the enemy army. Holland provides an evocative description:
The enemy directly in their path ... realised to their horror that [the Athenians], far from providing the easy pickings for their bowmen, as they had first imagined, were not going to be halted ... The impact was devastating. The Athenians had honed their style of fighting in combat with other phalanxes, wooden shields smashing against wooden shields, iron spear tips clattering against breastplates of bronze ... in those first terrible seconds of collision, there was nothing but a pulverizing crash of metal into flesh and bone; then the rolling of the Athenian tide over men wearing, at most, quilted jerkins for protection, and armed, perhaps, with nothing more than bows or slings. The hoplites' ash spears, rather than shivering ... could instead stab and stab again, and those of the enemy who avoided their fearful jabbing might easily be crushed to death beneath the sheer weight of the advancing men of bronze.
The Athenian wings quickly routed the inferior Persian levies on the flanks, before turning inwards to surround the Persian centre, which had been more successful against the thin Greek centre. The battle ended when the Persian centre then broke in panic towards their ships, pursued by the Greeks. Some, unaware of the local terrain, ran towards the swamps where unknown numbers drowned. The Athenians pursued the Persians back to their ships, and managed to capture seven ships, though the majority were able to launch successfully. Herodotus recounts the story that Cynaegirus, brother of the playwright Aeschylus, who was also among the fighters, charged into the sea, grabbed one Persian trireme, and started pulling it towards shore. A member of the crew saw him, cut off his hand, and Cynaegirus died.
Herodotus records that 6,400 Persian bodies were counted on the battlefield, and it is unknown how many more perished in the swamps. The Athenians lost 192 men and the Plataeans 11. Among the dead were the war archon Callimachus and the general Stesilaos.
In the immediate aftermath of the battle, Herodotus says that the Persian fleet sailed around Cape Sounion to attack Athens directly. As has been discussed above, some modern historians place this attempt just before the battle. Either way, the Athenians evidently realised that their city was still under threat, and marched as quickly as possible back to Athens. The two tribes which had been in the centre of the Athenian line stayed to guard the battlefield under the command of Aristides. The Athenians arrived in time to prevent the Persians from securing a landing, and seeing that the opportunity was lost, the Persians turned about and returned to Asia. Connected with this episode, Herodotus recounts a rumour that this manoeuver by the Persians had been planned in conjunction with the Alcmaeonids, the prominent Athenian aristocratic family, and that a "shield-signal" had been given after the battle. Although many interpretations of this have been offered, it is impossible to tell whether this was true, and if so, what exactly the signal meant. On the next day, the Spartan army arrived at Marathon, having covered the 220 kilometers (140 mi) in only three days. The Spartans toured the battlefield at Marathon, and agreed that the Athenians had won a great victory.
Mound (soros) in which the Athenian dead were buried after the Battle of Marathon
The dead of Marathon were buried on the battlefield. On the tomb of the Athenians this epigram composed by Simonides was written:
Fighting in the forefront of the Hellenes, the Athenians at Marathon destroyed the might of the gold-bearing Medes.In the meanwhile, Darius began raising a huge new army with which he meant to completely subjugate Greece; however, in 486 BC, his Egyptian subjects revolted, indefinitely postponing any Greek expedition. Darius then died whilst preparing to march on Egypt, and the throne of Persia passed to his son Xerxes I. Xerxes crushed the Egyptian revolt, and very quickly restarted the preparations for the invasion of Greece. The epic second Persian invasion of Greece finally began in 480 BC, and the Persians met with initial success at the battles of Thermopylae and Artemisium. However, defeat at the Battle of Salamis would be the turning point in the campaign, and the next year the expedition was ended by the decisive Greek victory at the Battle of Plataea.
All sources and credit to: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_of_Marathon
http://greece.greekreporter.com/files/Marathon-Battle.jpeg
http://greece.greekreporter.com/files/Marathon-Battle.jpeg